Types of Mold: A Complete Guide
Mold is a common problem that can affect homes, offices, and even outdoor areas. While it might seem harmless at first, mold can cause serious health issues and damage to buildings if left untreated. Understanding the different types of mold is important because each type comes with its own risks and requires different ways to handle it. In this blog, we’ll cover the most common types of mold you might encounter, how they can affect you, and why calling Mold Inspection and Testing Experts is often the best first step.
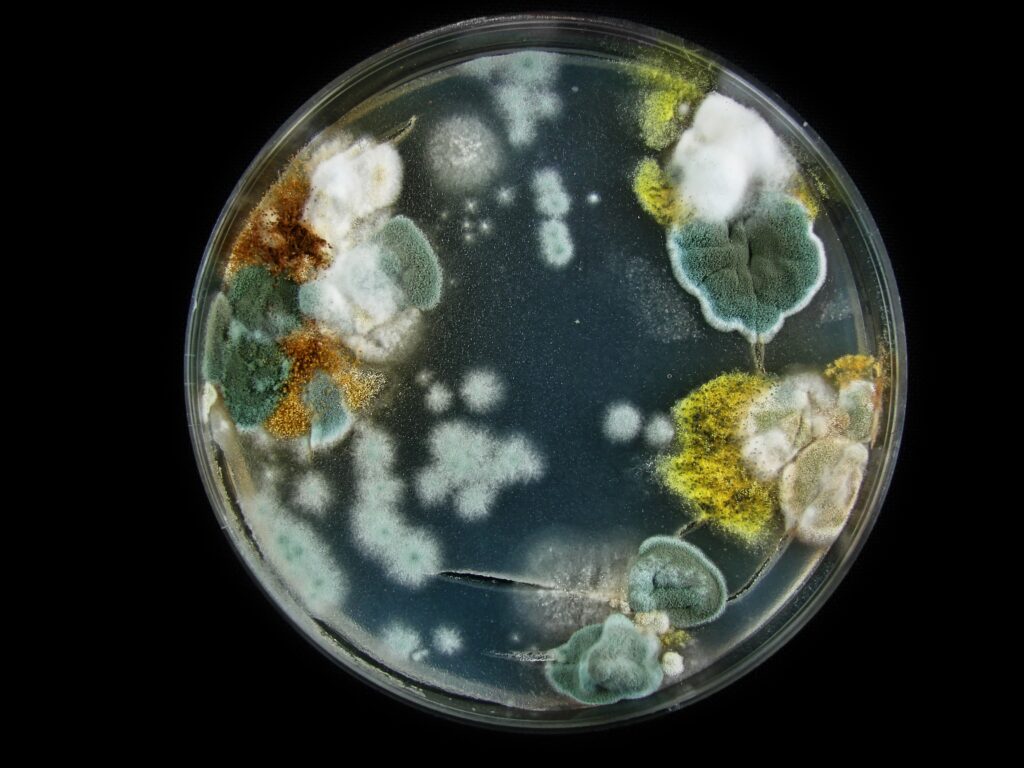
What Is Mold?
Mold is a type of fungus that grows in damp, warm, and humid conditions. It reproduces by releasing tiny spores into the air, which can settle on surfaces and start growing if the environment is right. Mold can be black, green, white, orange, or even pink, depending on the type. Some molds are harmless, while others can cause serious allergies, respiratory problems, or even toxic reactions.
Now, let’s dive into the different types of mold you should know about.
Common Types of Mold
1. Aspergillus
Aspergillus is one of the most common types of mold found indoors. It appears in many colors, including green, yellow, and black. This mold usually grows on walls, insulation, clothing, and food.
- Health Risks: Aspergillus can cause allergic reactions, respiratory infections, and a condition known as aspergillosis, especially in people with weakened immune systems.
- Where It’s Found: Basements, bathrooms, kitchens, and anywhere with water damage.
2. Cladosporium
Cladosporium is another widespread indoor mold. Unlike many other molds, it can grow in cooler environments. It is often black or olive-green in color.
- Health Risks: Exposure to Cladosporium can lead to skin rashes, asthma attacks, sinus infections, and eye irritation.
- Where It’s Found: Carpets, wooden surfaces, fabrics, and heating and cooling ducts.
3. Stachybotrys (Black Mold)
Stachybotrys, commonly known as black mold, is infamous for being highly toxic. It has a dark green or black appearance and a slimy texture.
- Health Risks: Black mold produces mycotoxins that can cause severe respiratory problems, chronic fatigue, nausea, and even neurological issues.
- Where It’s Found: Water-damaged buildings, drywall, and ceilings.
If you suspect black mold, it’s crucial to contact Mold Inspection and Testing Experts immediately for a professional evaluation.
4. Penicillium
Penicillium is known for its blue or green color and can spread very quickly. While Penicillium is used to make antibiotics like penicillin, its presence indoors is not a good sign.
- Health Risks: Can cause allergies, asthma, and lung inflammation.
- Where It’s Found: Water-damaged mattresses, wallpaper, carpets, and ductwork.
5. Alternaria
Alternaria is one of the most common outdoor molds but often makes its way indoors through open windows and doors.
- Health Risks: Known to trigger asthma attacks and allergic reactions.
- Where It’s Found: Bathrooms, under sinks, around windows, and on shower walls.
6. Chaetomium
Chaetomium usually appears after water damage and has a cotton-like texture. It starts out white and eventually turns gray or black.
- Health Risks: Can cause skin and nail infections, and if inhaled, may lead to respiratory problems.
- Where It’s Found: Behind walls, in ceilings, and under floors where there has been water intrusion.
Less Common but Important Types of Mold
While the types listed above are the most common, there are other molds you should be aware of:
7. Fusarium
Fusarium thrives in cold, wet environments. It’s typically pink, white, or reddish.
- Health Risks: Can cause skin infections and eye infections and even more severe conditions like brain abscesses in rare cases.
- Where It’s Found: Carpets, wallpaper, and HVAC systems.
8. Aureobasidium
Aureobasidium is a mold that starts pink or brown and darkens over time. It’s commonly found on painted surfaces and behind wallpaper.
- Health Risks: Can cause eye, skin, and nail infections.
- Where It’s Found: Wooden furniture, window frames, and caulking.
9. Trichoderma
This fast-growing mold is usually white with green patches. Some species of Trichoderma produce mycotoxins.
- Health Risks: Respiratory problems and, in severe cases, building destruction due to its enzyme production.
- Where It’s Found: Wet drywall, wallpaper, and carpet.
List of Common & Uncommon Types of Mold
| Mold Type (Common Name) | Scientific Name | Common/Uncommon | Typical Locations Found |
| Aspergillus | Aspergillus spp. | Common | Walls, insulation, clothing, foods |
| Cladosporium | Cladosporium spp. | Common | Fabrics, carpets, wood, HVAC ducts |
| Black Mold | Stachybotrys chartarum | Common but dangerous | Water-damaged materials |
| Penicillium | Penicillium spp. | Common | Wallpaper, mattresses, insulation |
| Alternaria | Alternaria spp. | Common | Showers, sinks, damp places |
| Fusarium | Fusarium spp. | Uncommon | Water-damaged carpets, fabrics |
| Chaetomium | Chaetomium globosum | Common after flooding | Drywall, ceilings, musty smell |
| Mucor | Mucor spp. | Common | HVAC systems, damp carpets |
| Aureobasidium | Aureobasidium pullulans | Common | Behind wallpaper, painted wood, window frames |
| Ulocladium | Ulocladium spp. | Common | Severe water damage, grows with black mold |
| Trichoderma | Trichoderma spp. | Uncommon | Damp wood, paper, carpets |
| Epicoccum | Epicoccum nigrum | Uncommon | Drywall, wood, carpet |
| Dry Rot Mold | Serpula lacrymans | Uncommon | Wood, causes “dry rot” |
| Nigrospora | Nigrospora spp. | Uncommon | Airborne, sometimes found indoors |
| Wallemia | Wallemia sebi | Uncommon | Old food, salty/sugary environments |
| Acremonium | Acremonium spp. | Uncommon | Humidifiers, drain pans, cooling coils |
| Memnoniella | Memnoniella echinata | Uncommon | Wet materials, similar to black mold |
| Bipolaris | Bipolaris spp. | Uncommon | Indoor and outdoor locations |
| Curvularia | Curvularia spp. | Uncommon | Damp indoor areas |
| Basidiospores | Basidobolomyces spp. | Uncommon | Wood decay locations |
| Rhizopus | Rhizopus spp. | Uncommon | Rotting food, damp indoor areas |
| Geotrichum | Geotrichum candidum | Uncommon | Paper, fabrics, food |
How Mold Affects Health
Mold exposure doesn’t affect everyone the same way. Some people may be highly sensitive to even small amounts, while others may not show symptoms until the exposure is significant.
Common health problems caused by mold include:
- Sneezing and coughing
- Runny nose and congestion
- Eye irritation
- Skin rashes
- Headaches
- Fatigue
- Worsening of asthma symptoms
In severe cases, especially when toxic molds are involved, long-term exposure can lead to serious neurological and respiratory conditions.
If you experience any unusual health symptoms and suspect mold in your environment, it’s important to contact Mold Inspection and Testing Experts to assess and confirm the problem.

How to Identify Mold
Sometimes mold is easy to spot, it looks like dark patches on walls or ceilings, or you might notice a musty smell. However, not all mold is visible. It can hide inside walls, under flooring, and behind appliances.
Signs you might have a mold problem include:
- Musty odors
- Water stains on walls or ceilings
- Warped or stained wood
- Peeling paint or wallpaper
- Chronic allergy symptoms without a known cause
Professionals use tools like moisture meters, thermal imaging cameras, and air quality tests to detect hidden mold.
Why You Shouldn’t Remove Mold Yourself
It might be tempting to grab some bleach and scrub away the mold yourself. However, DIY mold removal can actually make the situation worse by spreading mold spores throughout your home.
Professional Mold Remediation Experts:
- Identify the type of mold
- Determine the source of moisture feeding the mold
- Safely contain and remove the mold
- Treat the area to prevent future mold growth
This is why hiring Mold Inspection and Testing Experts is essential for properly dealing with mold problems.

How to Prevent Mold Growth
While you can’t completely eliminate mold spores from your home, you can control moisture to prevent mold growth. Here are some tips:
- Fix leaks immediately
- Keep humidity levels below 60%
- Use exhaust fans in bathrooms and kitchens
- Clean and dry areas after flooding
- Regularly inspect roofs, pipes, and windows for leaks
- Use mold-resistant products when building or renovating
Being proactive is the best way to keep your home mold-free.
FAQs About Types of Mold
1. What causes mold to grow inside homes?
Mold grows when there is excess moisture combined with organic materials like wood, drywall, or fabric. Common causes include leaks, poor ventilation, and high humidity levels.
2. How quickly can mold start growing after a water leak?
Mold can begin growing within 24 to 48 hours after a water intrusion if conditions are right.
3. Is all black-colored mold dangerous?
Not all black molds are toxic. Some black molds are relatively harmless, but Stachybotrys chartarum (“black mold”) is particularly dangerous and needs professional attention.
4. Can household cleaners like bleach completely kill mold?
Bleach can kill surface mold on non-porous materials, but it often fails to penetrate porous surfaces like drywall, where mold roots can survive and regrow.
5. Are there natural ways to prevent mold growth?
Yes, using dehumidifiers, improving ventilation, fixing leaks quickly, and using natural mold inhibitors like vinegar or tea tree oil can help prevent mold growth.
6. Can mold grow in air conditioning systems?
Yes, mold can easily grow in HVAC systems, especially if there is moisture buildup or clogged drains. Regular maintenance helps prevent this.
7. What are “toxic molds” and how are they different from other molds?
Toxic molds, like some strains of Stachybotrys or Trichoderma, produce mycotoxins, which are toxic compounds that can severely impact human and animal health, unlike most common allergenic molds.
8. Can mold spread from one part of a house to another?
Absolutely. Mold releases airborne spores that can travel through ventilation systems, windows, doors, and even on clothing and pets, spreading easily if not contained.
9. How do professionals test for different types of mold?
Mold Inspection and Testing Experts use air samples, surface samples, moisture mapping, and laboratory analysis to accurately identify mold types and contamination levels.
10. Is it possible to completely remove all mold from a building?
It is nearly impossible to eliminate all mold spores, but professional remediation can remove active mold colonies and reduce spore levels to safe, manageable levels.
Conclusion
Mold can seem like just a minor annoyance, but it can lead to serious health and property issues if ignored. Knowing the different types of mold and how they affect you is key to protecting your home and your health. If you notice any signs of mold, it’s best to call Mold Inspection and Testing Experts to accurately identify the problem and handle it safely.
By staying informed and taking quick action, you can keep your indoor spaces healthy, safe, and mold-free.